What is market mode?
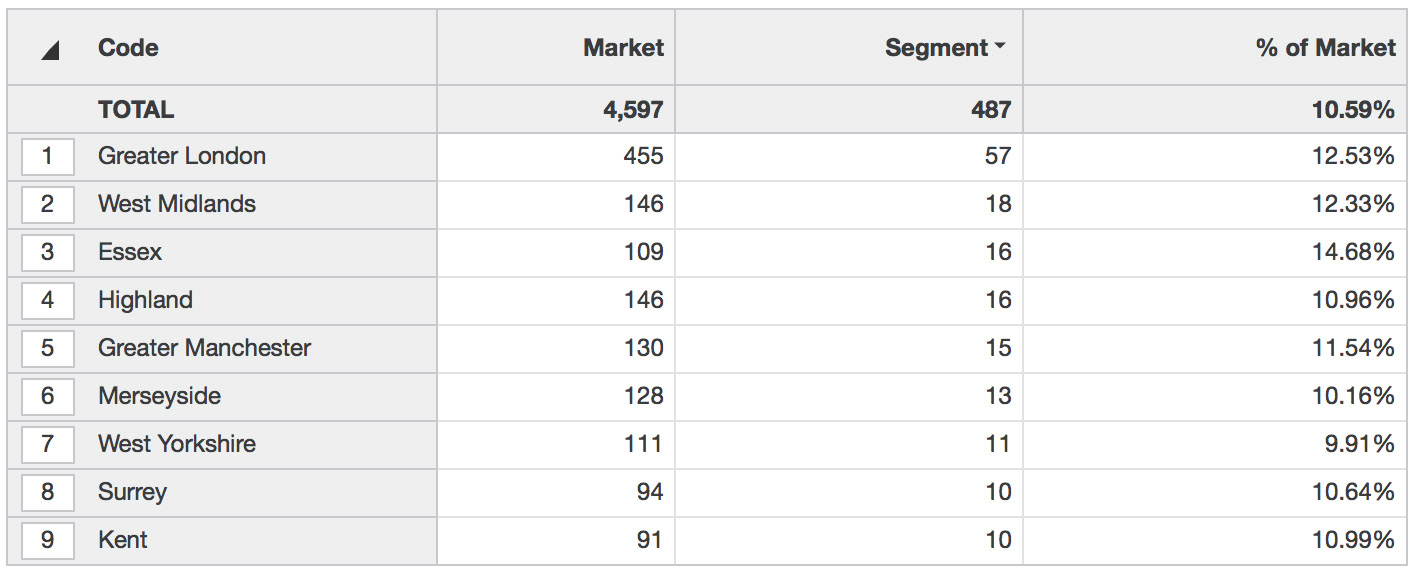
Market mode can be used to show market penetration. Looking at the first line in the image below, the total market in Greater London is 455 customers, but only 57 of those customers are buying this segment (the selected product groups), giving a market penetration of 12.53%. This example uses a 'count' measure, but other measures such as value or quantity could also be used.
How it works
Process | Actions | What happens in the grid |
|---|---|---|
Step 1 | Make selections (and focus) in the usual way. | Anything focused on before entering market mode is the market. Results appear in the 'market' (first) column. |
Step 2 | Choose market from the mode button. | |
Step 3 | Make more selections (and focus) in the usual way. | Anything focused on after entering market mode is a segment. Results appear in the 'segment' (second) column. |
Step 4 | Choose what you want to count (from the orange drop down box) | Additional market, segment and % of market columns appear for each measure selected. |
Step 5 | If required, also choose your measure(s). You can also choose no measures. | |
Step 6 | Click on the dimension most relevant to your analysis. | View and analyse your results. |
Example
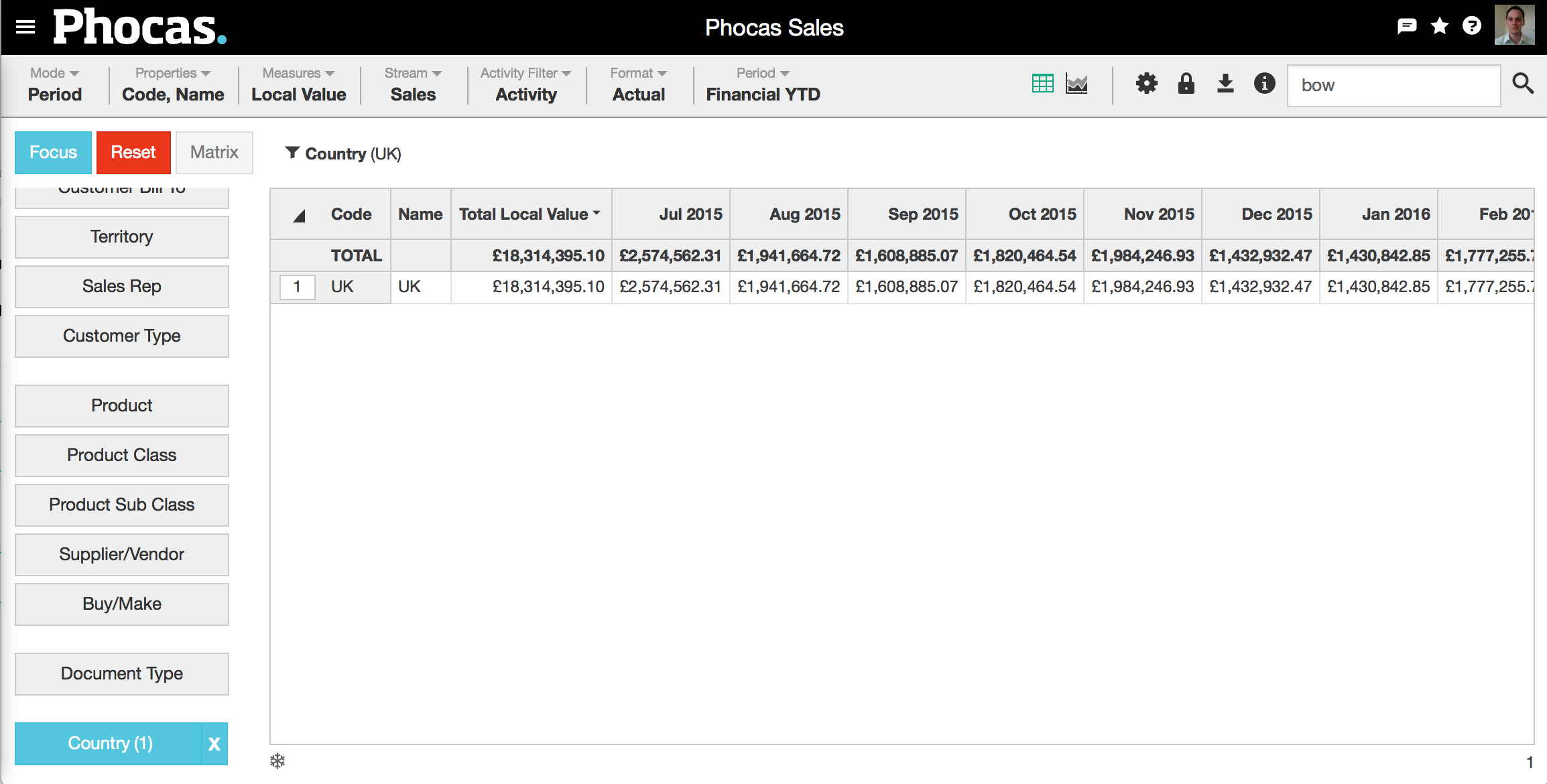
1. Choose your market | Do this by choosing a dimension and making selections as usual. In this example, we've chosen UK from the Country dimension, as shown. |
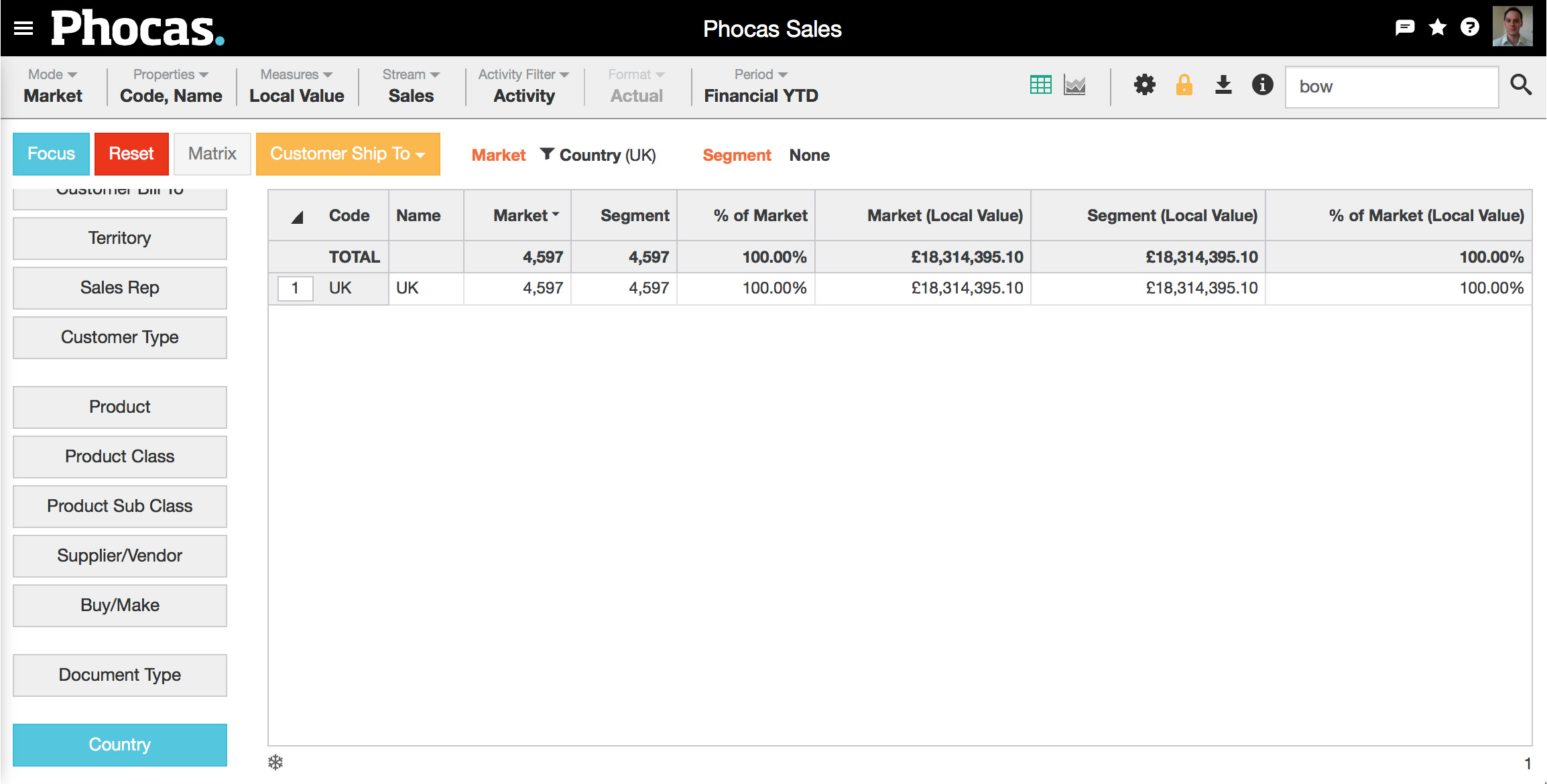
2. Select market mode | Choose Mode > Market. Three things will occur:
|
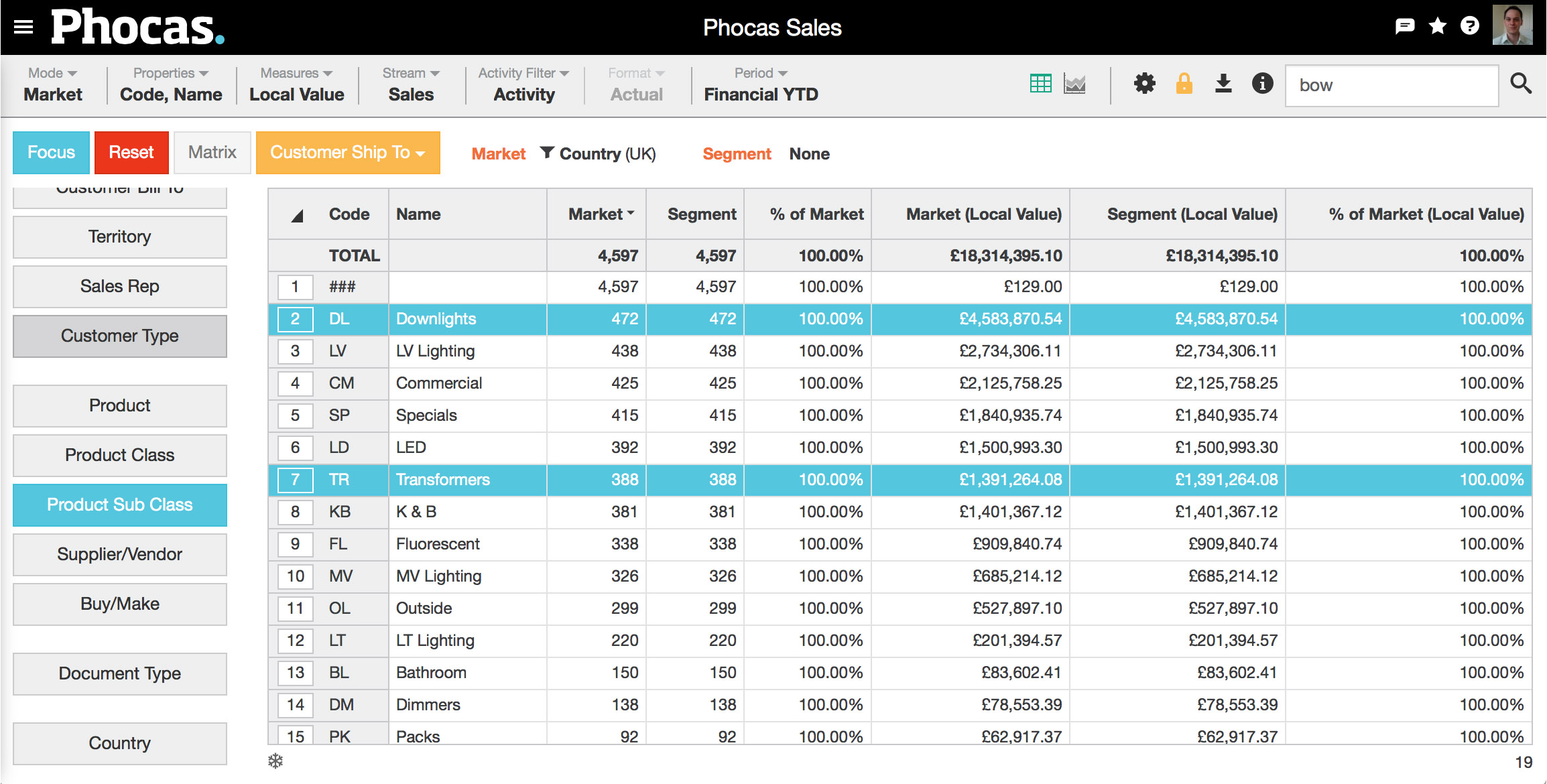
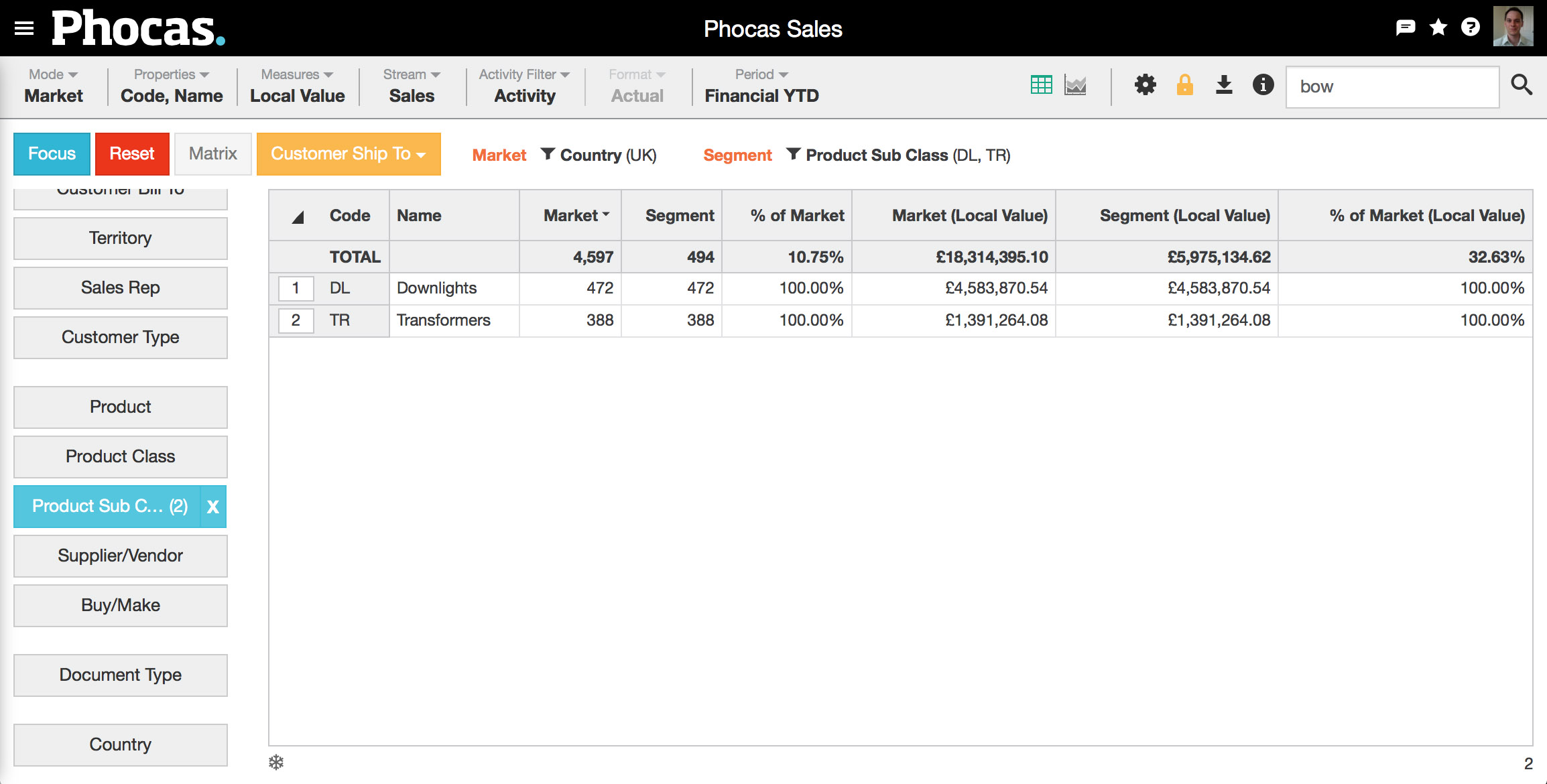
3. Choose your segment | Segment your selection. In this example, we've chosen downlights (DL) and transformers (TR) from our Product Sub Class dimension. This is done in the usual slice and dice manner: select and focus. Two things will occur:
|
|
4. Choose what to count | From the orange dropdown box, define your market by selecting what you'd like to count. In this example we've selected Customer Ship To, so the number of customers will define our market. You could also count branches, or stores, or any of your dimensions. |
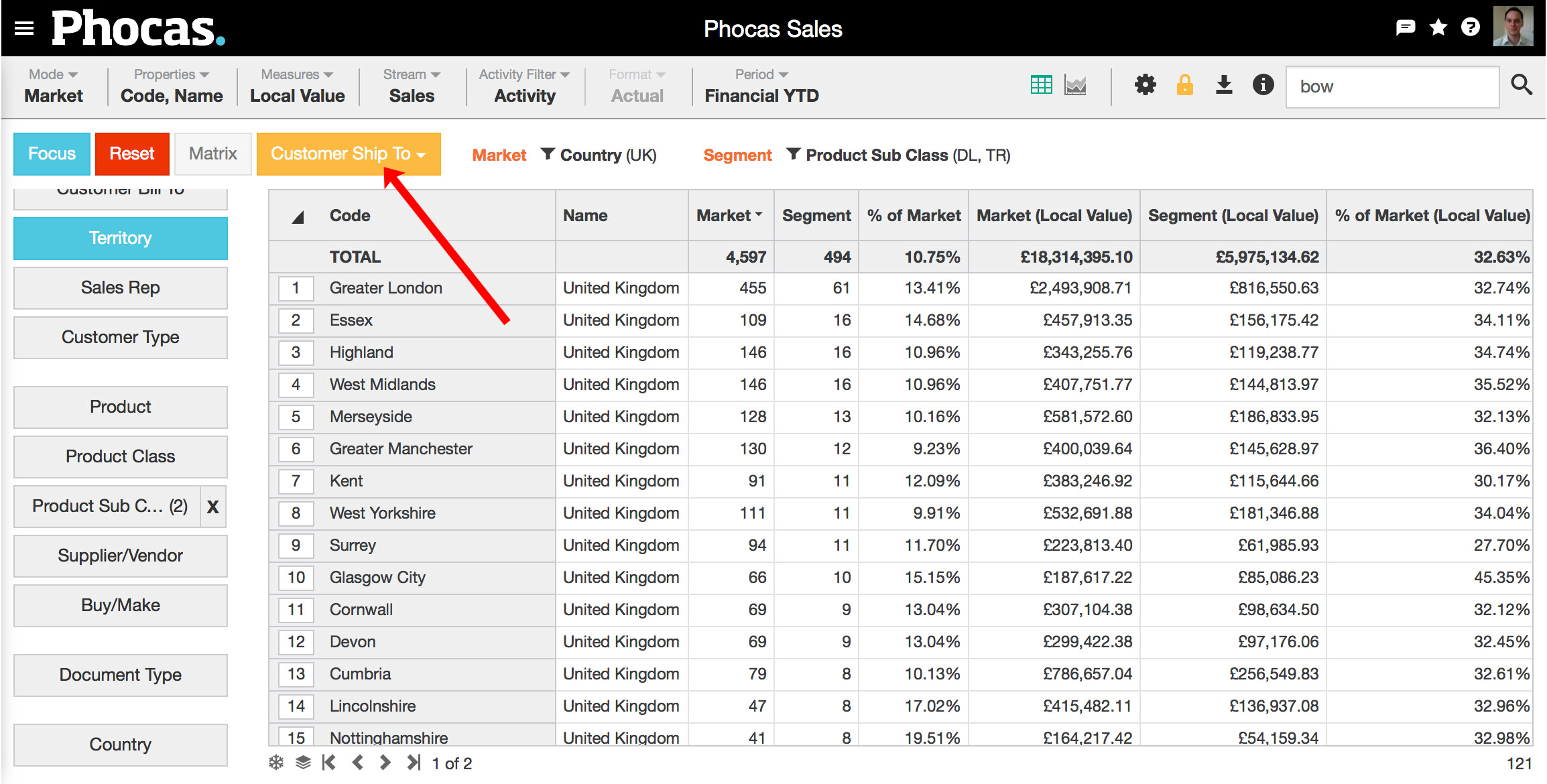
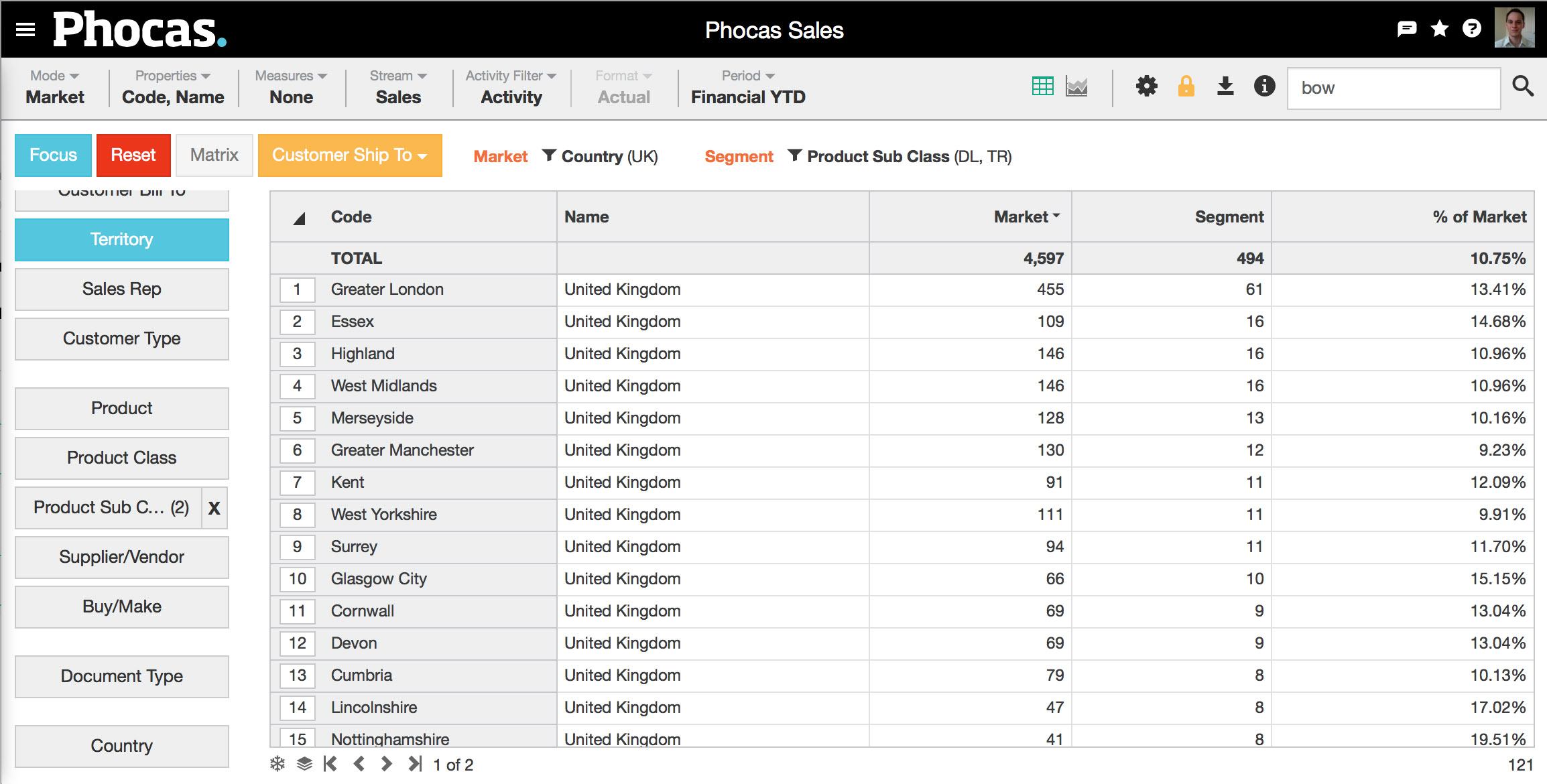
4. View and analyze | Click on the appropriate dimension for your analysis. In this example, we've chosen the territory dimension. Choose the appropriate measures. In this example we've chosen None, which simplifies the grid by removing three columns. Viewing these results shows, for example, that of the 109 customers in Essex, only 16 are purchasing our segment (downlights and transformers). |
While still in market mode, you can make changes to your segment by clearing current selections and selecting/focusing on other data. The 'Segment' status bar will update accordingly. However, you can't change the market. To set a different market you need to start again.
Notes:
The 'market' will only include selections that have activity in the period.
Market mode can't be charted.
Video
Overview video on the Phocas Academy.
Impact on performance
| Note |
|---|
Market mode can have a major impact on performance, especially on large databases. While it can be used effectively on general queries, caution should be used when using this option on a collection of dashboard widgets, as the compound impact on performance can be severe. |